WHAT IS SCREENING
Screening should be offered to all women irrespective of their age. Reach out to a gynecologist near you for the same. Now a days , a Combined 1st Trimester Screening test ( NT NB ultrasound scan with double marker blood test before 13.5 weeks ) is considered best.
It aims to identify women with a higher risk when the diagnostic test needs to be performed. A screening test can never confirm a fetus as having Down syndrome.
WHAT IS DOWN SYNDROME
Down syndrome refers to intellectually challenged individuals with unique physical characteristics due to trisomy 21 (presence of extra copy of chromosome no 21 ). It occurs in 1 in every 800 pregnancies.
Risk of having a baby with Down syndrome is related to mother’s age
25 year woman – 1 in 1200
35 year woman – 1 in 350
40 year woman – 1 in 100
WHY SCREEN FOR DOWN SYNDROME
Down syndrome is the commonest cause of intellectual disability among live born babies which can be detected during pregnancy.
30% of down syndrome pregnancy die during early pregnancy .
There is no associated major structural defect detectable on routine prenatal ultra sound.
Individuals have long life often reaching adulthood hence big social and financial burden in caring for such individuals.
HOW TO SCREEN FOR DOWN SYNDROME:-
1st trimester ultrasound
Includes evaluation of gestational age, nuchal translucency ( fluid behind the neck of the baby), presence of nasal bone, fetal heart rate ,Ductus Venosus flow, tricuspid regurgitation , Uterine artery PI and ruling out other structural anomalies, are additional features about fetal well being.
BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS:-
1 . Double marker – (1st trimester < 13 weeks ) blood test of mother to find levels of hormones free beta HCG and PAPP A MOM . Their values are combined with ultrasound parameters and mother age and a probability of down syndrome is calculated. PAPP A MOM levels also help predict risk of developing hypertension in mother and risk of growth retardation of the fetus.
2. TRIPLE TEST / QUADRUPLE MARKER – (2ND TRIMESTER 15 – 19 WEEKS )
Their accuracy is much lower than the double marker.
triple screening measures AFP ( alpha fetoprotein), HCG ( human chorionic gonadotropin )and uE3 (estriol) When hormone inhibin A is also added it is called quadruple marker. The amount of these substances helps your doctor find out the chance that your baby has birth defects like Down syndrome, spina bifida or anencephaly. These tests can not show for sure that your baby has a birth defect.
If a screening test comes as SCREEN POSITIVE, diagnostic test will be needed to confirm it.
FALSE POSITIVE – 5% The odds of the fetus being affected when screen is positive is between 1 in 30 and 1 in 20 .
Prenatel screening for Down syndrome is still an informed choice and the couple has the right to decide.whether they would like to go through screening or not.
3. NIPT: It is a non invasive test which uses mothers blood. It is 99 % accurate. It can be offered to women who have missed a Double marker or in those with advanced maternal age ( >40 years) who have no structural defect on good quality ultrasound( documenting NT, NB, DV flow, uterine artery PI etc)
NIPT screens for –
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome)
Trisomy 13 (Ptau Syndrome)
Though few labs do many more chromosomes testing, their accuracy has not been established.
4. Invasive test
4a. CVS (Chorionic villus sampling) done between 10 -13 weeks or
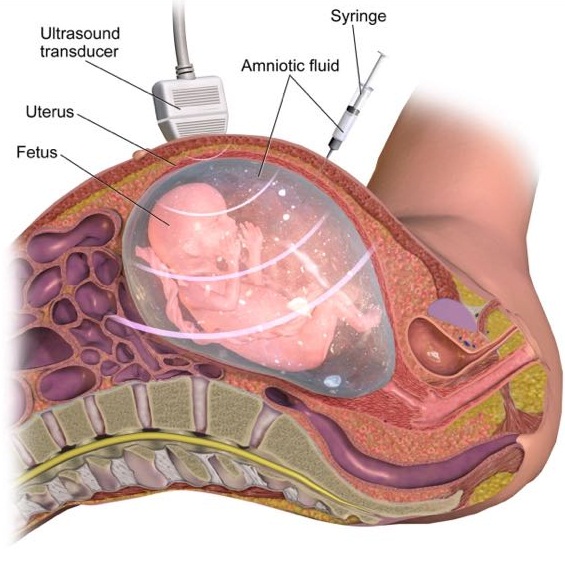
4b. Amniocentesis done between 16 –18 weeks.
These genetic test analyse baby’s own genetic material, collected from the amniotic fluid or placenta by a fetal medicine expert.
The results are considered 100% accurate.
These procedures have complications but generally safe in experienced hands.
The genetic material obtained is send for FISH/ Karyotyping/Microarray.